Electric motors are at the heart of every automated system. You can find them in vehicles, medical devices, robots, construction machines, and kitchen appliances. This is why, at DMKE, we ensure our clients get the highest quality motors, whether they need a simple BLDC, a brushed one, or any other.
In this article, we’ll discuss some common types of electric motors and will shed light on the working mechanisms and more. So, read on:
How Do Electric Motors Work?
Electric motors work along the basic idea of converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. This conversion occurs through the one-on-one working of the magnetic fields and current.
When a machine is turned on, the electric current flows through its coil. The flow of the current results in a force, known as the Lorentz force, which causes the rotor to spin. The spins are pushed to the surrounding systems that then power up the devices and help them function.
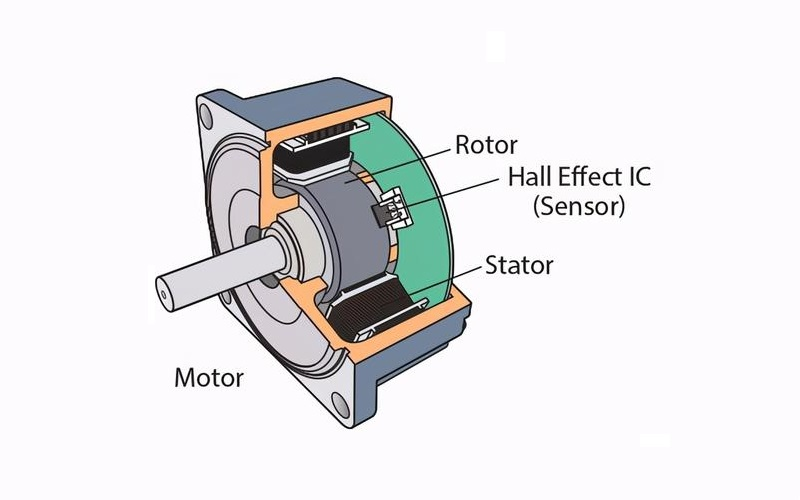
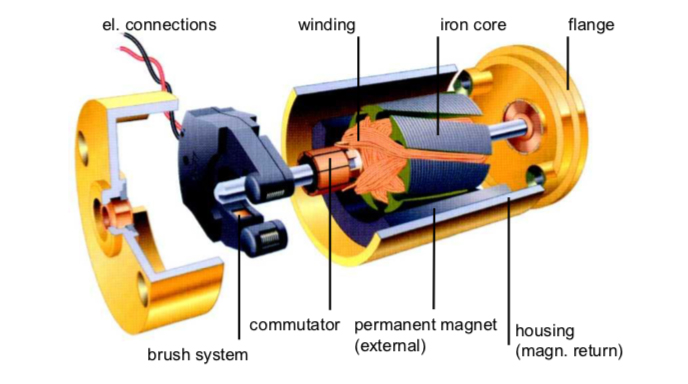
All electric motor and controller combos have three major parts:
- A stator, which is a stationary magnetic field.
- A rotor, which is the main rotating element.
- A commutator, which directs proper current flow.
Depending on its complexity and design, a motor can either run on direct current (making it DC) or alternating current (making it AC). Each of these offers different functionality and advantages.
Mechanisms Behind Motor Rotation

Although the basic working of an electrical motor has already been discussed, it is crucial to understand the rotation and the principles that lie underneath thoroughly. For a better idea of an electric motor and other systems, it is important to grasp how electric current interacts with the magnetic field.
Simply stated, the current flows through the conductor placed inside a magnetic field. This current moves towards the magnetic field. This flow of current makes the magnetic field experience a force called the Lorentz force. This force moves the conductor and the overall magnetic field.
The electric motor and drive systems are designed in a way that starts with a signal to the conductor. This converts into rotations that continue using coils and magnets. Inside every electric motor, the stator and the rotor work in collaboration. The stationary stator generates a magnetic field, and the rotor rotates under the influence of electromagnetic forces.
When AC or DC flows through the stator, a mobile magnetic field is created that interacts with the rotor’s magnetic field. This produces a rotational force that moves and powers the device’s machinery. This rotational force is known as torque in physics.
Regardless of the size, type, and functional complexity, the underlying principles of physics remain the same. That is, all motors work when electrical energy is converted into efficient rotational and motional energy.
Differences Between The Working Of Varying Motor Types
Inside DC motors, commutators and brushes maintain a proper direction of current flow. Here, it is ensured that the rotor spins in only one direction.
Alternatively, AC motors work with alternating current frequency changes, maintaining continuous motion without the use of brushes. This helps AC motors stay low-maintenance and also have high efficiency output.
Further, advanced devices have brushless DC motors that use electronic controllers to switch current and improve speed.
In any automatic appliance, the synergy and connection between the electric motor and controller are important to ensure precise speed and control. This connection is what helps the modern automation systems, transport means, and robots to work effectively.
Electric Motors and Their 10 Common Types: An Overview

Depending on the purpose a motor serves, the design and performance index vary, along with motor applications. Understanding the different types of electric motors and their applications can help engineers, buyers, and customers find the most efficient type depending on their needs.
To better understand each type of electric motor and its differences from others, one can categorise them into two groups as follows:
1- Classification based on current and commutation type
2– Classification based on special functional features
Below, we’ll look at the main types and a few sub-types of these classes in detail:
Classes Based On Types of Current And Commutation Type
This class includes the AC and DC motors and the subtypes of each.
- Common types of AC motors include AC servos, asynchronous, and synchronous motors.
- On the contrary, DC motors subtypes include brushed DC motors, brushless DC motors, DC servos, and a few others.
AC Electric Motors
AC motors use alternating current to ensure reliable, low-maintenance, and continuous performance. These motors are primarily found in setups where a smooth, high-power output is required.
They are famous for their ability to ensure steady torque, making them perfect for large-scale industrial systems and applications that demand longer and stable operation. AC motors can be found almost everywhere, from machinery to robots, and from factories to home appliances, and in every machine that requires a consistent power source.
The common types of AC motors include the following:
- Synchronous Motors: The AC synchronous motors work by rotating at a speed similar to that of the stator’s magnetic field. Irrespective of the load faced, the speed here remains constant. These motors are mostly used in devices where ensuring a consistent speed is important, e.g., clocks, watches, records, and more.
- Asynchronous Motors: Commonly known as Induction motors, these AC motors rotate slightly faster than their magnetic field. Known for their durability, these motors are used in fans, compressors, and industrial equipment.
- AC Servo Motors: The AC servo motor is the most common AC motor subtype, designed to offer high precision within a closed-loop control system. These motors are commonly used in CNC machines, packaging systems, and small robots, where accurate positioning, real-time feedback, and consistent speed are extremely important.
DC Electric Motors
As is evident from their names, DC motors operate on direct current and are known for providing precise output in terms of torque and speed. The main advantage of DC motors lies in their smooth startup and quick response. This is what makes them ideal for high-speed automated processes and portable systems.
A few common sub-types of DC motors include the following:
- Brushed DC Motors: A brushed motor is a conventional motor that uses brushes and a commutator to transfer current to the rotor. These motors offer a wide range of electronic control, but they are also prone to wear over time. They are commonly used in home appliances, toys, and automotive systems.
- Brushless DC Motor: A BLDC Motor is a compact motor that operates on direct current. It is highly efficient and produces almost no noise, making it perfect for use in drones, small water pumps, and indoor cooling systems, where its silent operation is nothing short of a blessing.
- Micro BLDC Motor: As the name indicates, this is a brushless DC motor that is extremely small in size and is often used in places where space is limited but power output cannot be compromised. The most common applications of this motor include its use in medical devices, hand-held tools, and compact IT setups.
- DC Servo Motors: DC servo motors are brushless motors designed to deliver energy, precision, and efficiency in a compact design while running on batteries. These motors are mostly used in robots, automated vehicles, and wheel hubs of AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) to provide powerful control, e-mobility, and ensure smooth operation.
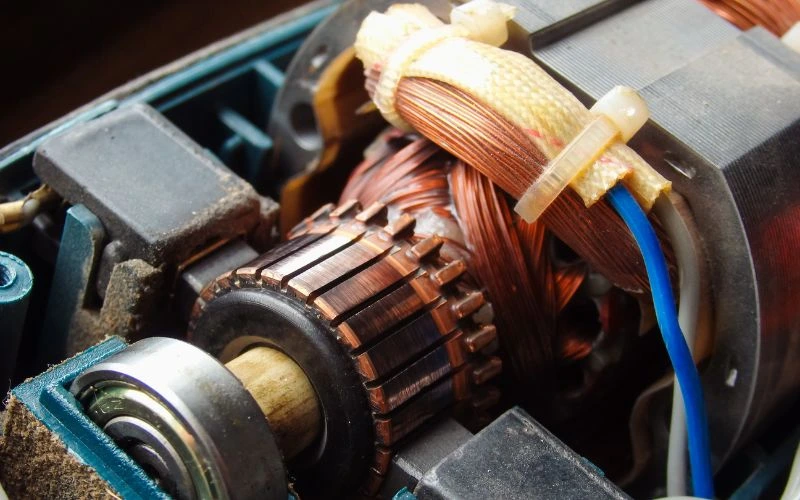
Classification Based On Special Functional Features
This group refers to electric motors and systems that are created to perform a distinctive mechanical function in a specialised environment.
- Common specialised motors include explosion-proof motors, stepper motors, torque motors, and a few others.
Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are designed to move in discrete steps instead of continuous rotation. This unique motion allows them to offer precise positional control. These motors are commonly found in 3D printers, CNC machinery, medical equipment, cameras, and optical systems.
Explosion-Proof Motors
Explosion-proof motors are designed for hazardous environments where chemicals, gases and dust are common. Their specialised build prevents internal sparking, overheating, and interaction with external contaminants, while ensuring optimal performance.
These motors are used in mines, labs, and the oil and gas industries, where safety and durability are needed.
Step-by-Step Guide To Selecting the Right Motor
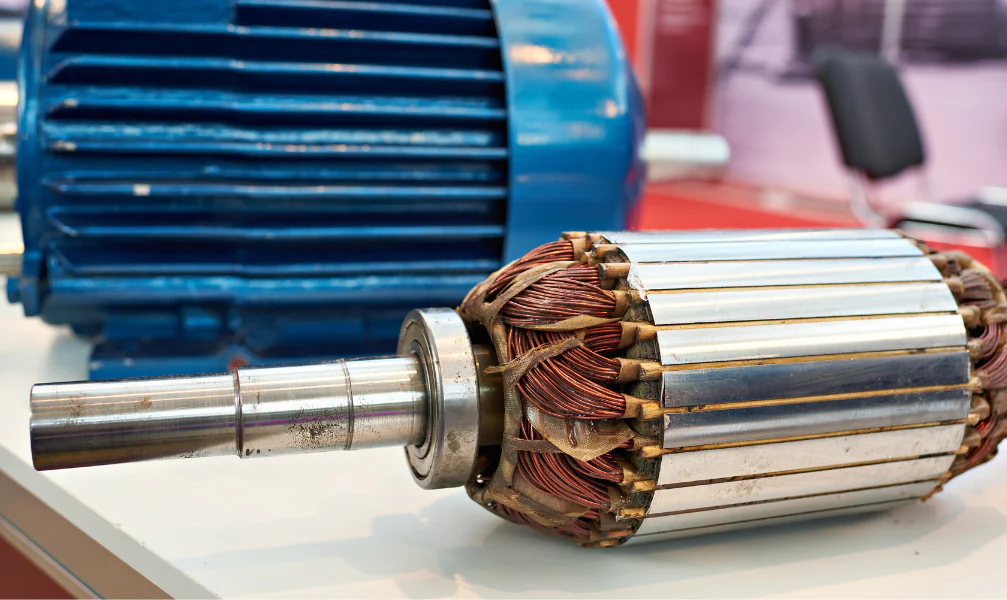
Considering the wide variety, choosing the right electric motor and drive system can be a little difficult and time-consuming. Sometimes, even professional engineers struggle with choosing the right motor and connector.
However, with an idea of how to go about choosing a motor, you can easily find one that will help achieve efficiency, precision, and reliability for your specific needs. Below is a step-by-step guide to select the right motor depending on your needs, environment, and expectations from the device:
Step 1: Define Your Application Requirements
The first step is to be clear on the function that you would want a motor to perform. Whether you need continuous rotations, variable speeds, or dynamic positioning, it is important to know the motor’s functionality in a device to choose the right kind.
If possible, try to identify whether the motor will be loaded constantly, will have a variable load type, or would work best with shock loading. Lastly, calculate the required speed and torque that will help ensure optimal performance as per your needs.
Step 2: Choose Motor Type
Once you have defined the applications of the motor, you can choose any of the above-discussed motor types.
If you want continuous high-power applications, you can go for AC motors. For variable speed operation and precise control, DC motors are ideal. If you need a maintenance-free motor that is also compact and efficient, go for a brushless DC motor. For accuracy and automation, go for servo motors. Alternatively, stepper motors are excellent for motion control.
Below is a table that explains which specific motor type works best in a particular device:
| Motor Type | Suitable Applications |
| AC | Pumps, fans, blowers, conveyors, HVAC systems |
| DC | Electric vehicles, heavy-industry equipment, forklifts, cranes, variable-speed drives |
| Brushless DC (BLDC) | Robots, AGVs, smart drones, modern medical devices |
| Servo | CNCs, automatic arms, automation lines |
| Stepper | 3D printers, cameras, and medical equipment |
| Explosion-Proof | Mining, oil & gas, chemical plants |
| Frameless BLDC | Robotic joints, small automation tools |
| Underwater BLDC | Marine robots, submersibles, and underwater pumps |
| DC Servo + Planetary Gear | AGVs, conveyor systems, and lifting mechanisms |
| AGV Servo Drive Wheel | Automated guided vehicles, logistics robots |
Step 3: Considering External Conditions
Once you have decided on the type of motor you want, it’s important to see whether or not your selected type is suitable for the environment it will work in. For example, if a motor has to work in hazardous environments like mines or chemical plants, it must be explosion-proof.
For outdoor usage, investing in a motor that is not waterproof or rust-resistant is not very wise. Also consider whether the selected type works well with the temperature, moisture, and vibration levels of the machine or place where it will be used.
Step 4: Find A Compatible Controller For the Motor
It’s essential to find control systems that are compatible with the electric motor and its operation. This helps achieve stable speed and torque while ensuring long life and durability for the motor. It’s best to conduct proper research and find efficient motor drivers and inverters that will smoothly accelerate and brake the motor system.
Step 5: Evaluate Efficiency and Maintenance
Depending on the motor you have selected, evaluate the overall efficiency as well as maintenance needs. This helps ensure that the selected one is the optimal choice for the device under consideration.
Choosing a low-maintenance motor with high energy efficiency will help you stay stress-free for a long time. It will also ensure that you make no compromise on the performance and efficiency of the motor.
Other than these important steps, below are some tips that will help one choose the right motor:
- Carry out proper and in-depth research before making any purchase decision.
- Never fall for scammers offering poor-quality motors at an unbelievably low price.
- Try to buy a motor with at least 20% higher torque than your requirement, just to be on the safe side.
- Only purchase the electric motor and controller from trusted and reliable makers.
- Verify that the motor’s voltage ratings match your area’s power supply standards.
- Try to choose a motor that offers waterproofing, thermal protection, and rust-resistance.
- Prefer motors that have overload sensors to prevent hazards.
- For rigorous outdoor usage, only go for sealed or waterproof motors.
- When purchasing a motor for medical or official settings, find options with low noise and lower vibration features.
- Always go to a seller who offers good after-sales support and part availability.
Components in Motor Development

Crafting a quality and high-performance electric motor and drive system is a task that requires precision, expertise, and advanced materials. Motor development is not something every brand can do with exceptionality. Hence, it is essential to find reliable manufacturers and suppliers of motors whenever you need one.
To understand the components required in motor development, one can divide them into two different groups based on their functionality and role in the working of the motor. Below is a detailed discussion of each of these component groups, one by one.
1- Base Components
A total of five elements make up the foundation of all types of motors. These include the stator, rotor, bearing, shaft, and the motor frame or housing. These components form the heart of every electric motor, and in most cases, any issue with one of these causes the motor’s failure.
The two main elements, i.e., stator and rotor, work together to create mechanical motion, while bearings ensure the smooth rotation of the rotor and other parts during the motor’s operation. Shafts inside the motor help transmit torque to the load, and lastly, the motor housing or frame, as its name explains, protects the internal parts from dust, moisture, vibration, and heat.
It is essential for these core elements to have high-quality and insulating properties. This will help ensure the durability and proper functioning of a motor, along with preventing energy loss and overheating.
2- Electrical and Control Elements
Equally important to the core components of a motor are its electrical and control elements. These include the windings, the commutator or electronic controller, the sensors, and the drivers and inverters that help the motor perform its function.
Windings, typically made of copper, help generate the magnetic field when a motor is turned on. An electronic controller or commutator ensures proper current flow and continuous rotation inside a running motor. Within these controllers are the sensors, drivers, and inverters that help regulate the speed, direction, and torque of the motor.
These electrical components, along with the control systems, make the motor efficient, stable, silent, and responsive.
Other than these core components, modern motors also feature advanced technologies and systems for thermal management, magnetic selection, and smart control. Engineers carefully consider magnetic material selection and structural design to craft motors that are not only durable but also high-performing.
Some motors used in modern automation, AGVs, and underwater pumps are equipped with explosion-proof components for added protection and longevity.
At DMKE, we engineer each and every electric motor and drive solution using high-quality materials, followed by advanced manufacturing processes. All our products undergo extensive tests for quality and performance before they are marketed to consumers.
This careful formulation ensures that every motor we manufacture delivers stability, power, and performance like none other.
Conclusion
Regardless of its type, each motor works on the basic principle of converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. All motor types, from DC to AC, and from brushless to brushed motors and their subtypes, serve a specific purpose. Each of these have their own strengths and weaknesses that make it ideal for particular applications.
Understanding the basic features and advantages of each motor type helps one easily find an electric motor and drive system that best suits their needs.
At DMKE, every motor we develop is built with precision, durability, and the user’s ease in mind. This ensures that our motors deliver consistent performance and reliability for years to come.
We deal in almost all types of AC and DC, brushed and brushless motors, along with AGV and explosion-proof motors. Whether you want to empower your industrial machines or are building a DIY kitchen appliance that needs a reliable motor, our products cater to everyone.
Contact us today to get a customised motor solution that best caters to your specific needs and applications.