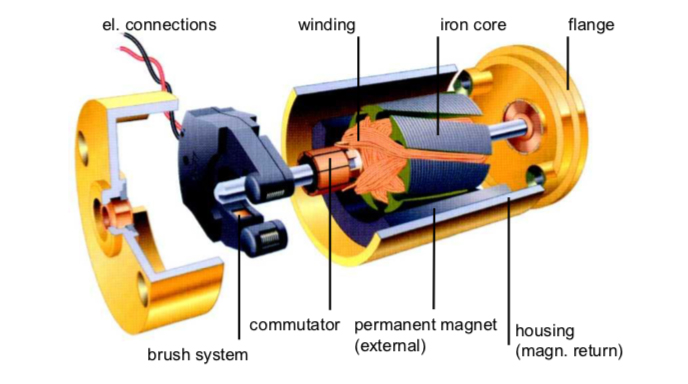
If you work in an industry that relies on accurate, stable, and consistent performance and output, you need a reliable and stable system at its back. This system must work in a clear-cut, consistent, and controlled repetitive mechanism.
When engineers go about finding the right servo solutions for their projects, they are met with confusion and incomplete information that leaves them confused. Whenever they try to understand how a servo motor achieves perfection and precision, the answers they get are often in the form of intricate formulas, signals, and theories.
For non-technical people from procurement departments, as well as novice engineers, this heavy information often brings no benefit. It rather creates a learning barrier that is very hard to fill.
In reality, the working of a servo motor is not at all complicated. It’s just that there are rarely any proper explanations to help the common people understand how it works. In simple words, you can easily understand the working of a servo motor by understanding the mechanism of movement from the real world.
In this guide, we will be doing exactly that. Before we delve into the steps of a servo motor’s working, we are going to connect the entire concept to a real-world instinctive movement, so you can better understand everything.
The Human Analogy: How Our Hands Mirror Servo Control?

To understand the basic working mechanism of a servomotor, you can simply look at how you pick up things in real life. For example, you can imagine yourself reaching out to pick up a glass or cup of water.
If you break this entire process into micro steps, it will start with your brain deciding that you want to pick something up. Upon deciding, the brain will send signals to your hand to carry out the motion of picking up the glass. At this time, your eyes will constantly stay focused on the movement of your hand.
In case your hand goes in another direction where the glass is far away from you, your brain will instantly correct you and help you quickly pick up the glass. This is a loop of command, action, observation, and correction. This loop is a repetitive one that helps us humans perform our daily tasks without any problems.
This is exactly how a servo system works. It is a coordinated system that works on the loop of command, action, observation, and correction using the following components:
- The controller, which plays the role of the brain of the servo system.
- The servo motor itself, which acts like the arm and performs the movement.
- The encoder, which acts as the eyes of the system, will monitor the workflow and report back in case a correction is needed.
Now that you have understood the basic relationship, a deeper understanding of the servo-electric motor working can be very easy.
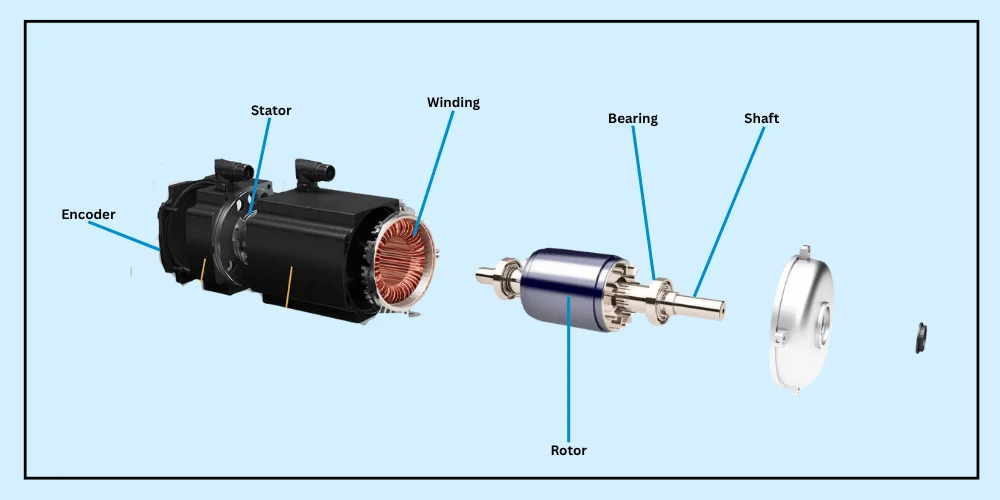
The Three Core Components of a Servo System
Before we jump into the core components and technical details, we want you to remember one thing: Everything in the working of a servo motor is precisely connected to another thing. When you understand everything with this idea at the back of your mind, the entire understanding will be smooth.
- Controller: The “Brain” That Plans Every Move
The controller of a servo motor decides what should happen. For example, it decides how far the motor should move, how fast and smooth it should be, and where the final positioning should rest.
The controller prepares and executes the entire motion plan of a motor once it is turned on. It sends the command back to the motor and also receives feedback from the encoder to see whether or not any correction is needed. It is an important part of the servo motor, without which no movement can take place.
The better the controller is, the better it will plan and inspect, and then the better the overall working of the motor.
- Servo Motor: The “Arm” That Performs the Action
The role of the motor is to convert electrical input into mechanical output. It will rotate, hold, accelerate, or decelerate exactly as instructed and demanded by the controller.
If the motor is stable, it will result in smoother motions with consistent output and torque, as well as fewer vibrations. This motor is mainly what decides the precision in robotics, AGVs, and other automation systems.
- Encoder: The “Eyes” That See and Report Back
The encoder is a consistent monitor of the system. It keeps everything in control by measuring the position, angle, speed, and movement at every instant, and quickly sends this information back to the controller.
If there is extra load on the motor, if it drifts, overshoots, or lags, the encoder will immediately report it to the brain of the system. This way, it ensures a smooth and instant correction. The better and higher-quality the encoder is, the better the accuracy it will provide.
How Servo Motors Work: A Step-by-Step Workflow
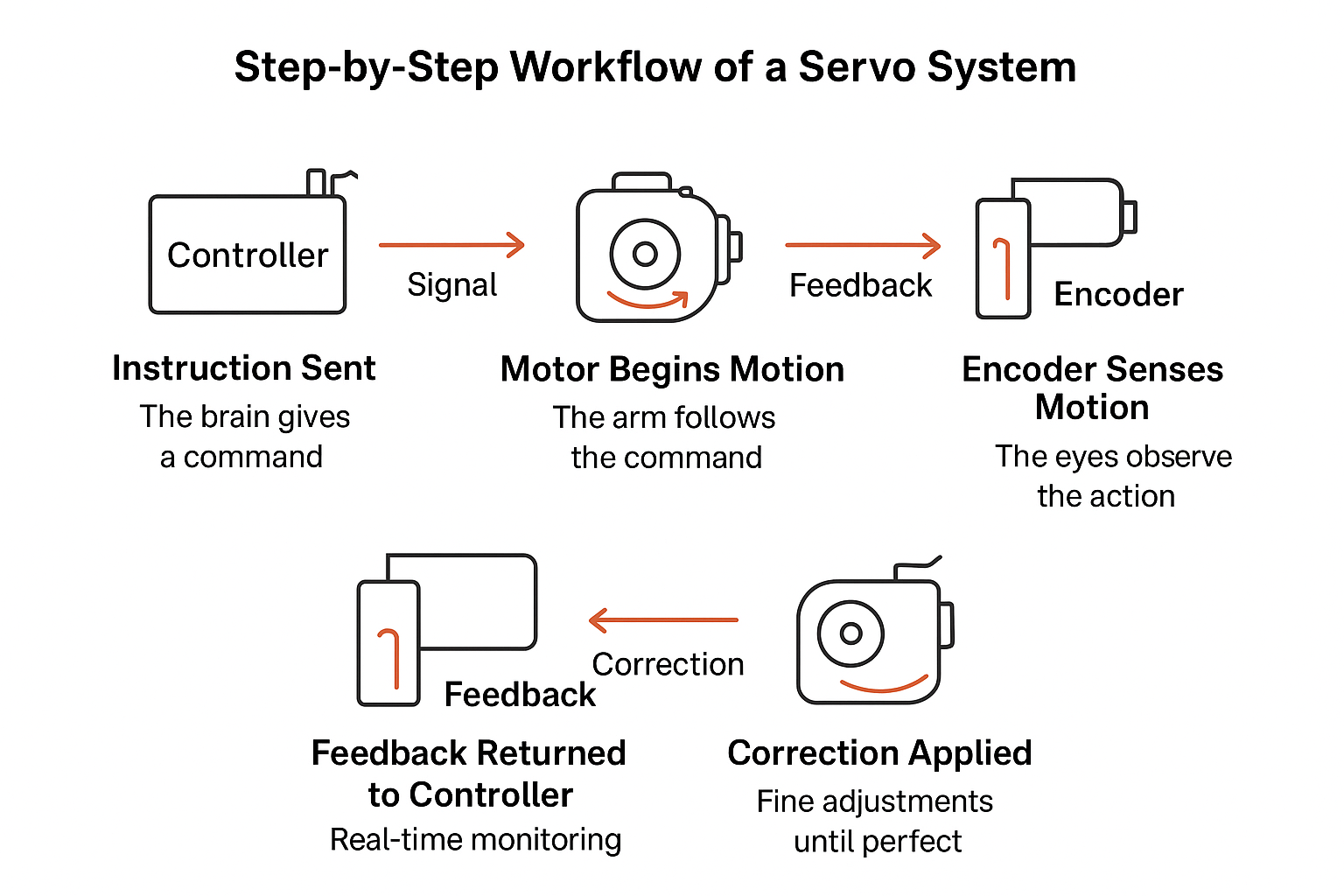
Understanding the technical working of a servo system becomes easy when you break it down into clear, interrelated steps. You can think of the entire work as a choreographed dance, where every move smoothly follows the previous move, guided by corrections as well as feedback, while ensuring perfect coordination.
Below is the stepwise breakdown of the workflow of a servo system.
Step 1 — Instruction Sent (The Brain Issues a Command)
As with any movement in the human body, the working process of a motor also begins with the controller, which acts as the brain of the system. Consider how a human brain decides to pick up a glass of water. Similarly, the controller in a motor will decide what it should do.
In other words, the controller will decide the rotation angle, positioning, follow, as well as the speed. Once the decision is made, the controller sends the instruction as an electrical signal to the motor.
Since this is the first stage that initiates the working of a system, the clarity and accuracy at this stage are uncompromisable. If the controller sends weak or improper signals to the motor, the movement will be off from the beginning, thus resulting in the disrupted working of the overall system.
Depending on its type, the controller may use pulse-width modulation, analogue modulation, or digital communication to send a proper command precisely to the motor.
Step 2 — Motor Begins Motion (The Arm Follows the Command)
Once the instruction has been properly received, the motor will start springing into action. The action of the motor at this stage is directly dependent on the command given to it in the form of an electrical signal. Based on whatever signal it receives, the motor will either move linearly, rotate, or hold a specific position in a consistent manner.
Relating it to the real-life analogy, you can understand this step as your arm moving forward to grab the glass of water. In this stage, the quality of the motor and its internal components matters a lot. If the motor is stable and made with high-quality components, it will smoothly react to the signal without causing any vibrations or overshooting.
For industrial applications and robotics, smooth motion ensures exact positioning and decision regarding where the parts should be placed and how the machinery should operate.
Step 3 — Encoder Senses Motion (The Eyes Observe the Action)
While the motor is moving, the encoder will continuously keep tracking it for its position, accuracy, speed, and rotation angles. This is just like your eyes observing your arms as they reach for the glass. The encoder then sends the feedback to the controller based on whatever observation it has made.
Step 4 — Feedback Returned to Controller
Once the controller gets the feedback, it compares the actual working with the desired working of the motor. If there is any difference, it will immediately calculate the necessary adjustments to be made.
Step 5 — Correction Applied
Finally, the controller will send the correct messages to the motor, adjusting speed, torque, rotation angle, and everything else until the target working and positioning has been achieved. This happens many times during the working of a motor, even when the apparent motion seems seamless.
In real life, it would be like your hand nudging itself and altering its movements to go directly to the glass instead of somewhere else.
Why This Closed-Loop Principle Matters in Real Applications?
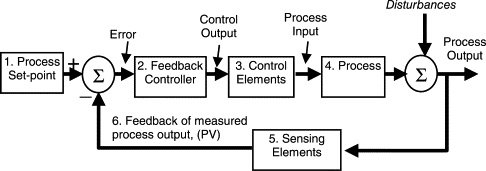
Precision and repeatability are two of the best features of any closed-loop servo system. Closed-loop systems offer continuous check and correction of tiny events even before the issue escalates. This closed-loop feedback is what helps a servo ensure a consistent movement without drifting, even under changing external conditions.
In a closed-loop system, the performance stays protected despite the shifting external loads. Compared to this, in an open-loop setup, added weight or external resistance goes unnoticed. This slowly grows and gradually affects the entire working of the system. Whereas in the closed-loop, feedback will instantly go to the brain, which will make quick adjustments, preventing the machines from dropping under heavier loads or falling out of sync.
Another notable advantage of a closed-loop system is its responsiveness. In such a system, corrections happen in real-time, and the setup doesn’t have to wait for one issue to be fixed before moving ahead. In simpler words, the corrections are made along with the working of the motor taking place.
This not only reduces downtimes and overshoots but also smoothens out everything and shortens the time taken by the system to come back to its original position. Such a feature is extremely important in fast-moving packaging lines, assembly stations, and other tools that depend on quick and stable action.
In a closed-loop system, tuning and maintenance become more practical compared to an open-loop one. Since the system is already measuring and monitoring itself and its aspects, engineers find it extremely easy to quickly fine-tune the parameters with confidence and with less chance of an error.
Below is a quick comparison of a closed-loop and an open-loop system for a clearer understanding:
| Feature | Open-Loop System | Closed-Loop System |
| Feedback | None | Real-time feedback via encoder |
| Accuracy | Lower, prone to drift | High, automatic error correction |
| Responsiveness | Fixed, cannot adjust | Instant adjustment to changes |
| Stability under load | Can shift or overshoot | Maintains position even with load changes |
| Complexity | Simple, cheaper | More complex, requires an encoder and a controller |
| Applications | Simple motors, basic automation | Robotics, CNC, precision automation |
What Actually Affects Servo Performance?
There are several interconnected factors that define how well and how accurately a servo system will perform. The major ones include the following:
1- Motor Stability: Smoothness and seamlessness of rotations and a smooth, consistent torque output, along with lesser vibrations, directly influence the quality of the motor’s motion. A stable system responds cleanly and seamlessly towards the commands it gets. The more stable a system is, the better it will respond to commands and changing loads.
2- Encoder Accuracy: Better resolution of the encoder directly translates into detailed and clear feedback. An encoder that is able to detect the tiniest of changes is a blessing. It can encode directly and send flawless information to the controller, offering better and faster motor performance.
3- Driver Algorithm Quality: The better algorithm of a driver helps with better interpretation of feedback and adjustment of current, speed, and torque. A refined algorithm means better responsiveness overall, reduced overshoot, and better motor performance even during rapidly changing loads.
4- Load Variation: Changes and differences, such as sudden changes in the load, will show how well and how tightly-knit the system of a motor is. A motor with stronger correction and feedback ability will perform better even under consistently shifting conditions.
5- Mechanical Build and Assembly: Misaligned, backlashed, and loosely coupled motor components will reduce the overall system’s precision. Even the best motors fail to perform if their mechanical setup and construction are not up to the mark.
6- Environmental Factors: Things like external temperature, dust, vibration, and humidity will definitely affect the overall working of the system. It is advisable to buy a motor only after checking its IP rating and ensuring that it is suitable for the environment in which it will be used.
How DMKE Ensures Reliable and Precise Servo Performance?
Once you understand the factors that affect the performance of a servo motor, it becomes clear why quality components inside a motor and rigorous testing prior to its usage and sale are so important.
At DMKE, our engineers and technicians focus on the tiniest of details during motor development to provide you with products that are reliable and precise and have an accurate output. All our servo products are engineered to ensure smooth, stable torque output, resist vibrations, and maintain their accuracy even under high loads.
Once you pair them with high-quality encoders, these motors will provide you with proper feedback. These motors will ensure a proper closed-loop feedback system that allows the controller to monitor and enhance the overall performance of the system.
At DMKE, the drivers we use in our motor are optimised with advanced algorithms. Our drivers come with the ability to properly translate the feedback and take immediate adjustment-related actions, while also reducing the noise and vibrations during operation.
We not only use quality components inside the system, but also make sure that each and every component undergoes strict internal testing, including an 8-step procedure to check load-time relations, long-run cycles, and precision. This guarantees consistent performance throughout all our products and makes us a capable supplier for bulk orders.
Designed for industrial usage, DMKE servo motors offer a wide range of practical uses in the robotics, EGV, and CNC industries, including other automation lines. All our products are capable of dealing more nicely and intelligently with variable loads and changing external conditions without ruining the performance.
High-quality parts, careful calibration, and rigorous testing are what set DMKE products apart from other motors. This is exactly why all our motors deliver precision, stability, and reliability like none other.
Start Making Smarter Motor Choices With DMKE!
Now that you clearly understand the working of a servo motor and have realised why a closed-loop control is important, it is easy to see how quality components and an accurate feedback system in any motor are important.
For engineers, stakeholders, industry owners, and procurers who are looking for reliable, precise, and quality motor solutions, DMKE offers several servo products that can provide proven performance.
All our motor solutions, including the custom servos, are made available to the clients only after passing strict internal 8-step testing and stringent quality control principles. Whether you need a motor for robotics, AGVs, CNCs, or any other automated industry setup, DMKE can help you choose the right servomotor without wasting your time.
Visit our website to explore DMKE’s servo product range and reach out to us today to get the best servomotor solutions for your needs.